Google reCaptcha V3 is the latest version provided with the highest security in comparison. Google contains different captcha services with reCaptcha V2. There are the (I am not a Robot) checkbox, invisible captcha and etc.
With the V3, Google guarantees zero friction while predicting the score for the website interactions. The score and the response report returned by the reCaptcha V3 is a very good security measure. It helps to take action accordingly to safeguard the website.
Like other Google reCaptcha concepts, the V3 also has more than one method to integrate the captcha challenge. Those are two as listed below.
- Programmatic invocation of the challenge.
- Automatic binding of the challenge with the form button.
This article explains to implement both methods by creating examples.
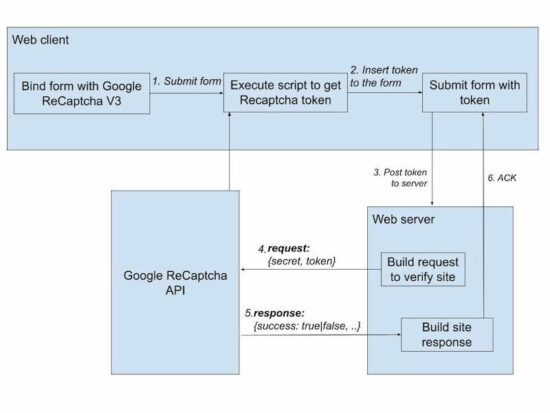
The below diagram will help to have a quick look at the Google reCaptcha V3 process flow. Continue reading to learn how to get the API keys and integrate reCaptcha for your website.
Read also,
If you prefer custom captcha code using PHP, you may check the linked article for example code.
How to get Google reCaptcha keys
This is a two-step simple process to get the API keys to add Google reCaptcha to a website.
These steps are listed below with screenshots.
- Register your site domain.
- Copy the reCaptcha site key and the secret key.
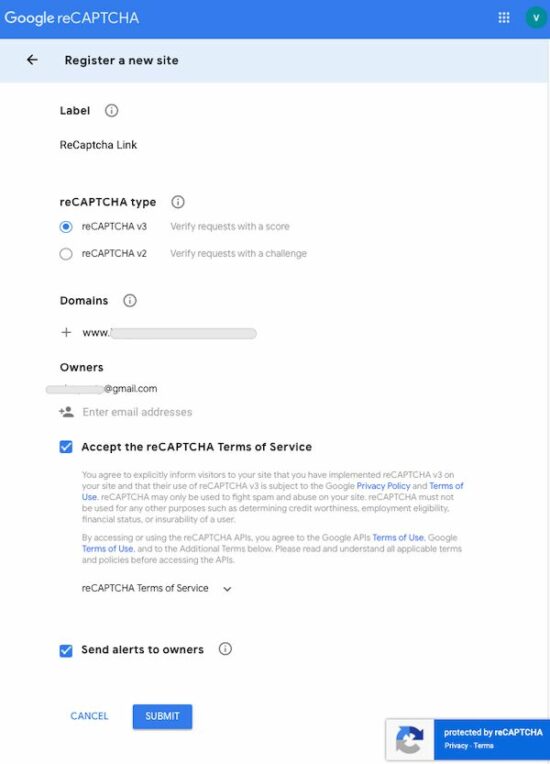
Step1: Register your site domain
Go to the Google recaptcha admin console to register a domain to integrate reCaptcha V3.
The below screenshot masked the data related to the domain and site owner details. Enter your site details in the place of the masked data.
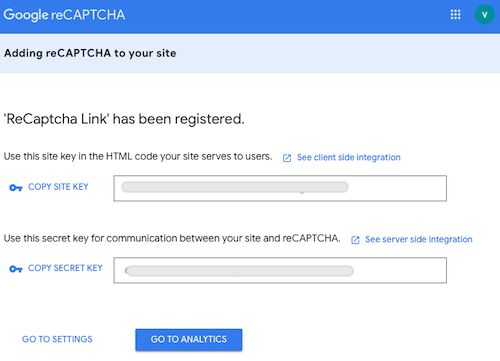
Step2: Copy the reCaptcha site key and the secret key.
Once registration is done, the reCaptcha V3 keys are displayed below. Copy these details and configure them into the website code.
The site key is used to render the Google reCaptcha on the client side. And, the secret key is used for server-side verification.
The following example contains an application configuration file for this. Continue reading to know how to configure.
About this example
This example renders the reCaptcha script and element in the landing UI. It has the configuration to make the website reCaptcha ready with the API keys.
It gets the token from the Google reCaptcha API and appends it to the form. On submit, the server-side PHP script receives the token to send the siteverify request to the API.
The reCaptcha API returns a JSON response with a score, success boolean, and more details. Based on the score (between 0 to 1), it helps to gauge the interaction’s standard. We have enabled a custom captcha solution based on the login validity standard.
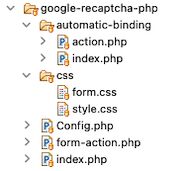
It integrates the Google reCaptcha V3 programmatic challenge in the root. If you want to implement the “automatic binding” method, then it is in a separate folder.
The below structure shows the reCaptcha example files order and location. It will be helpful to set up this code correctly in a development environment.
Application configuration file
It configures the Google reCaptcha V3 site and the secret keys used in the examples below.
The site key is used to render the Google recaptcha element on the client side. The secret key is used in the PHP files to build the site verification request parameters.
Config.php
<?php
class Config
{
const GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SITE_KEY = '';
const GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY = '';
}
?>
Method 1: Programatically invoking Google reCaptcha token via script
This method is used when the developer wants to have more programming control over the reCaptcha token.
During the explicit execution, it sets parameters to the request. These parameters can be returned with the Google reCaptcha V3 response. This will be helpful for additional verification.
HTML page renders form with reCaptcha JS
This landing page loads the JavaScript API while rendering the form UI. It uses the Google reCaptcha site key while loading the JavaScript.
index.php
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/Config.php';
?>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/form.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/style.css" />
<title>Form with Google reCaptcha V3</title>
<script
src="https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api.js?render=<?php echo Config::GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SITE_KEY; ?>"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="phppot-container tile-container">
<h3 class="text-center">Google reCaptcha V3</h3>
<form id="frm" name="frm" method="post"
onSubmit="getToken(event)">
<div>
<div class="row">
<label>Feedback</label> <input type="text"
name="txt_report" class="full-width" required>
</div>
<div class="row">
<input type="submit" value="Send" class="full-width">
</div>
<div id="ack-message"></div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Execute reCaptcha JavaScript API for token
It executes the Google reCaptcha request explicitly. The callback function of this action will return the reCaptcha token.
Then, the callback dynamically creates an input element using JavaScript. It loads the token to this element and appends it to the form.
After getting the token field, the form is submitted via JavaScript. The submitForm function posts the form data to the PHP via AJAX. In a previous article, we have seen how to enable PHP custom captcha using AJAX.
index.php (Javascript Google reCaptcha execute)
// Execute Google reCaptcha v3 to get token
function getToken(event) {
event.preventDefault();
grecaptcha.ready(function() {
grecaptcha.execute('<?php echo Config::GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SITE_KEY; ?>', { action: 'submit' }).then(function(token) {
var button = document.createElement('input');
button.type = 'hidden';
button.name = 'recaptcha_token';
button.id = 'recaptcha_token';
button.value = token;
var form = document.getElementById("frm");
form.appendChild(button);
submitForm();
});;
});
}
// Submit reCaptcha token to the PHP
function submitForm() {
const form = document.getElementById('frm');
const formData = new FormData(form);
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.open('POST', 'form-action.php', true);
xhttp.send(formData);
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhttp.readyState == 4 && xhttp.status == 200) {
document.getElementById("ack-message").innerHTML = xhttp.responseText;
document.getElementById('recaptcha_token').remove();
}
}
}
Verify website interaction using Google reCaptcha V3 API
The form submits action calls this PHP script by sending the reCaptcha token. It builds the post parameters with the Google reCaptcha v3 secret key and token.
This PHP script uses cURL to post the request to the reCaptcha API. The cUrl response returns the JSON data as given by the Google API.
It returns the score about the interaction made on the website. This score will be between 0.0 (lower) and 1.1(higher) ranking. It helps to predict the necessary steps to make to protect the site.
form-action.php
//PHP reCaptcha validation
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/Config.php';
$reCaptchaToken = $_POST['recaptcha_token'];
$postArray = array(
'secret' => Config::GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY,
'response' => $reCaptchaToken
);
$postJSON = http_build_query($postArray);
$curl = curl_init();
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_URL, "https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify");
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POST, 1);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $postJSON);
$response = curl_exec($curl);
curl_close($curl);
$curlResponseArray = json_decode($response, true);
if ($curlResponseArray["success"] == true && ! empty($curlResponseArray["action"]) && $curlResponseArray["score"] >= 0.5) {
mail("admin@site.com", "New report", $_POST["txt_report"]);
$output = "<div id='phppot-message' class='success'>Feedback received.</div>";
} else {
$output = "<div id='phppot-message' class='error'>Invalid request.</div>";
}
print $output;
exit();
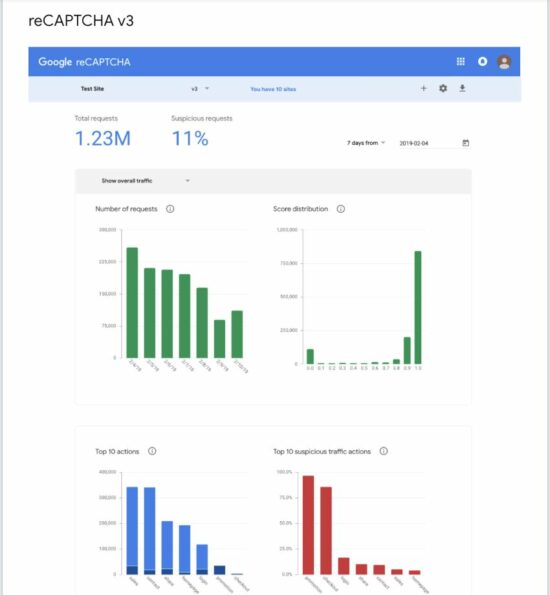
The reCaptcha admin console shows the analytics of site regarding the score distribution. See the below screenshot that displays the 4 types of graph provided by the analytics page for the reCapcha v3.
Method 2: Automatic binding callback with the submit button
This is a basic and simple method of integrating Google reCaptcha V3 for a site. In this automatic binding of the reCaptcha challenge, it gets the token in the callback.
Site HTML to bind the reCaptcha challenge automatically
It loads the Google reCaptcha JavaScript API as we did in method 1.
The g-recaptcha field binds the callback, action, and reCaptcha site key with the HTML5 data attributes.
automatic-binding/index.php
<?php
session_start();
require_once __DIR__ . '/../Config.php';
?>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./../css/form.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./../css/style.css" />
<title>Form with Google reCaptcha V3</title>
<script src="https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="phppot-container tile-container">
<h3 class="text-center">Google reCaptcha Automatic Binding</h3>
<form id="frm" name="frm" method="post" action="action.php">
<div>
<div class="row">
<label>Feedback</label> <input type="text"
name="txt_report" class="full-width" required>
</div>
<div class="row">
<input type="button" class="g-recaptcha full-width"
data-sitekey="<?php echo Config::GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SITE_KEY; ?>"
data-callback='onSubmit' data-action='submit'
value="Send" />
</div>
<?php
if (! empty($_SESSION["ack_message"])) {
?>
<div id="ack-message"><?php echo $_SESSION["ack_message"]; ?></div>
<?php
}
$_SESSION["ack_message"] = "";
?>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript callback to append token field to the form
This callback function is linked with the Google reCaptcha element, which is the send button of the form. So, on clicking the send button, it calls the onSubmit JavaScript function.
This callback has the reCaptcha token to be appended to the form data.
automatic-binding/index.php (JavaScript callback)
// JavaScript
function onSubmit(token) {
var button = document.createElement('input');
button.type = 'hidden';
button.name = 'recaptcha_token';
button.value = token;
var form = document.getElementById("frm");
form.appendChild(button);
form.submit();
}
PHP action to predict Google reCaptcha score
In PHP, it verifies the site and checks the interaction score. It contains the same code as the form-action.php we used in method 1.
The difference is that the response is sent via session instead of printing it to AJAX callback.
automatic-binding/action.php
//Google reCaptcha V3 server-side verification
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/Config.php';
$reCaptchaToken = $_POST['recaptcha_token'];
$postArray = array(
'secret' => Config::GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY,
'response' => $reCaptchaToken
);
$postJSON = http_build_query($postArray);
$curl = curl_init();
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_URL, "https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify");
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POST, 1);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $postJSON);
$response = curl_exec($curl);
curl_close($curl);
$curlResponseArray = json_decode($response, true);
if ($curlResponseArray["success"] == true && $curlResponseArray["score"] >= 0.5) {
mail("admin@site.com", "New report", $_POST["txt_report"]);
$output = "<div id='phppot-message' class='success'>Feedback received.</div>";
} else {
$output = "<div id='phppot-message' class='error'>Invalid request.</div>";
}
$_SESSION["ack_message"] = $output;
header("Location: automatic-binding.php");
?>
