This tutorial has a React NodeJS example for building a full-stack CRUD application. It gives easy guidelines to design the frontend and backend. The frontend React connects the NodeJS API controllers to interact for creating, reading, updating, and deleting. This will provide persistent storage with a MySQL database connected via API DAOs.
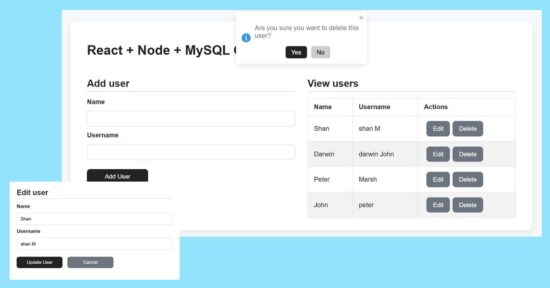
Add form design and user creation with NodeJS and MySQL
The user-create form contains only two fields to simplify the example. So, the React frontend assets manages states and props to carry these inputs’ data to post.
The addUser() props triggers the add action request to post the form data to the server.
It executes the insert query on clicking the ‘Add User’ button. The response will have the auto-generated key created on successful insert action of the CRUD functionality.
src/components/form/AddUserForm.jsx
import { useState } from 'react'
const AddUserForm = props => {
const initialFormState = { id: null, name: '', username: '' }
const [ user, setUser ] = useState(initialFormState)
const handleInputChange = event => {
const { name, value } = event.target
setUser({ ...user, [name]: value })
}
return (
<form
onSubmit={event => {
event.preventDefault()
if (!user.name || !user.username) return
props.addUser(user)
setUser(initialFormState)
}}>
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" value={user.name} onChange={handleInputChange} />
<label>Username</label>
<input type="text" name="username" value={user.username} onChange={handleInputChange} />
<div className="action-buttons">
<button type="submit">Add User</button>
</div>
</form>
)
}
export default AddUserForm
part of userControllers.js
export const addUser = (req, res) => {
const { name, username } = req.body;
db.query("INSERT INTO users (name, username) VALUES (?, ?)", [name, username], (err, result) => {
if (err) return res.status(500).json({ error: err.message });
res.json({ id: result.insertId, name, username });
});
};

Displaying user data rows with edit and delete action controls
The UserTable component displays the data table dynamically from the MySQL database. The prop.users tree map is used to form these rows to the UI.
Each row contains edit and delete controls that are bound to editRow and deleteUser functions respectively.
src/components/table/UserTable.jsx
import React from 'react'
const UserTable = props => (
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Username</th>
<th>Actions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{props.users.length > 0 ? (
props.users.map(user => (
<tr key={user.id}>
<td>{user.name}</td>
<td>{user.username}</td>
<td>
<button
onClick={() => {
props.editRow(user)
}}
className="button muted-button"
>
Edit
</button>
<button
onClick={() => props.deleteUser(user.id)}
className="button muted-button"
>
Delete
</button>
</td>
</tr>
))
) : (
<tr>
<td colSpan={3}>No users</td>
</tr>
)}
</tbody>
</table>
)
export default UserTable
In NodeJS the getUsers() module reads all users into an JSON response array as built below.
part of userControllers.js
export const getUsers = (req, res) => {
db.query("SELECT * FROM users", (err, results) => {
if (err) return res.status(500).json({ error: err.message });
res.json(results);
});
};
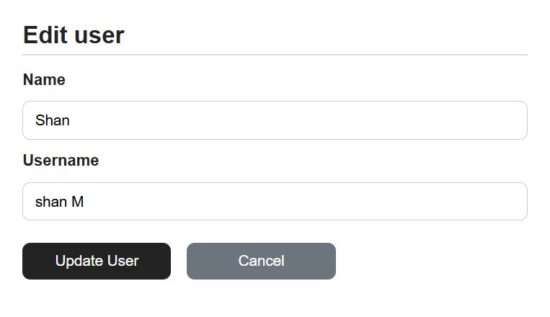
Updating current user by ID using update API in NodeJS
The add and edit forms are exactly same except that this edit form populated the existing user data. The currentUser props contains the exiting user details read by id.
On clicking the ‘Edit’ button the user id is passed to send the read request with the id.
Once the enduser edits the detail and submit, it request the NodeJS API to perform the update operation of the CRUD module.
Both add and edit button clicks prevents the default submit and requests the API via network call.
The edit form is used to view or edit the user details. When clicking cancel the editing directive is set to false to switch to the view mode.
src/components/form/EditUserForm
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
const EditUserForm = props => {
const [user, setUser] = useState(props.currentUser)
useEffect(
() => {
setUser(props.currentUser)
},
[props]
)
const handleInputChange = event => {
const { name, value } = event.target
setUser({ ...user, [name]: value })
}
return (
<form
onSubmit={event => {
event.preventDefault()
props.updateUser(user.id, user)
}}
>
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" value={user.name} onChange={handleInputChange} />
<label>Username</label>
<input type="text" name="username" value={user.username} onChange={handleInputChange} />
<div className="action-buttons">
<button type="submit">Update User</button>
<button onClick={() => props.setEditing(false)} className="button muted-button">
Cancel
</button>
</div>
</form>
)
}
export default EditUserForm
In the NodeJS, the backend user controller has an exclusive handle to prepare the user update query.
It binds the request parameter to the update query to go with the update operation.
part of userControllers.js
export const updateUser = (req, res) => {
const { id } = req.params;
const { name, username } = req.body;
db.query("UPDATE users SET name=?, username=? WHERE id=?", [name, username, id], (err) => {
if (err) return res.status(500).json({ error: err.message });
res.json({ id, name, username });
});
};
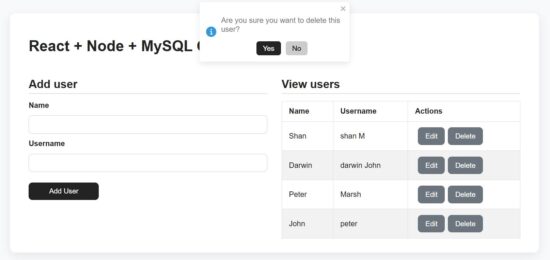
Deleting a user row via NodeJS controller
As like as an edit request, the delete action is also receives the user’s unique id in the request parameter.
The backend Node API receives the id and process the delete operation.
In the React frontend, it shows confirmation message in a toast box to avoid the mistakes.
part of userControllers.js
export const deleteUser = (req, res) => {
const { id } = req.params;
db.query("DELETE FROM users WHERE id=?", [id], (err) => {
if (err) return res.status(500).json({ error: err.message });
res.json({ message: "User deleted" });
});
};
How to run the React + NodeJS example?
Set up the MySQL database:
First find the /api/sql/users.sql file from the downloadable source code given in this React + NodeJS CRUD example.
Create a database and import that SQL script into that. Then Configure the database details to the db.js file in the NodeJS API root.
Start the backend NodeJS server:
Go to the NodeJS api path and start the server via npm. It will return the server running path http://localhost:5000/
In this example this backend api URL is configured with a specific constant for convenience. It avoid the overhead of changing in multiple places based on the environment.
cd /path/api
npm install
npm start
node server.js
Start the frontend React dev:
Go to the app location path and start the dev server. This will start the dev server http://localhost:5173/
cd react-node-mysql-crud-full-stack-tutorial
npm install
npm run dev
Conclusion
This tutorial built a simple code for React + Node.js + MySQL CRUD. The code for designing frontend and connecting the NodeJS API together gives a full stack execution sample. I hope, you learned how to read and display dynamic data from backend to React components and also how to manipulate them. The server controller is with appropriate cases to handle the CRUD with MySQL to store, retrieve, update, and delete data. With this base, it is easy to add more features to this CRUD utility.
References:
