Login form – an entry point of a website to authenticate users. PHP login system requires users to register with the application first to log in later.
The registered users are managed in a database at the back end. On each login attempt via the PHP login form, it verifies the database to find a match.
It is a very simple and essential job. At the same time, it should be designed with security to guard the site. It should filter anonymous hits 100% not to let unregistered users get in.
The PHP login form action stores the logged-in user in a session. It uses PHP $_SESSION one of its superglobals. It’s better to validate the existence of this session at the beginning of each page to be protected.
This PHP code can also be used to add an admin login for your control panel. Also, it can be used as a common authentication entry for both admin and user side of an application.
PHP login form code
This example is to design a PHP login form working with backend processing. The login page in PHP shows the UI elements like social login, forgot password and etc.
It posts data to process a username/password-based login authentication. This example uses the database to authenticate the user login.
This PHP login system is capable of linking the following code to the additional login form controls.
- Link PHP forgot/reset password feature.
- Link User registration PHP example to the sign-up option.
- Also, Link Oauth login with Facebook, Twitter and Linkedin.
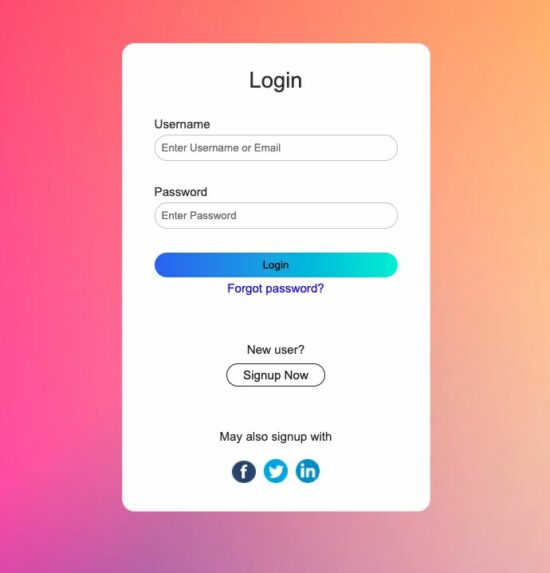
HTML form template
The landing page renders this template into the UI to let the user log in. It will happen when there is no logged-in session.
This form accepts the user’s login details username or email and a secure password. The submit event triggers the PHP login form validation and posts the login data to the PHP.
This PHP login form is responsive to the different viewport sizes. It uses simple CSS media queries for adding site responsiveness.
The form tag calls a JavaScript function validate() on the submit event. The below code includes the PHP login form validation script at the end.
view/login-form.php
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>User Login</title>
<link href="./view/css/form.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial;
color: #333;
font-size: 0.95em;
background-image: url("./view/images/bg.jpeg");
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<form action="login-action.php" method="post" id="frmLogin"
onSubmit="return validate();">
<div class="login-form-container">
<div class="form-head">Login</div>
<?php
if (isset($_SESSION["errorMessage"])) {
?>
<div class="error-message"><?php echo $_SESSION["errorMessage"]; ?></div>
<?php
unset($_SESSION["errorMessage"]);
}
?>
<div class="field-column">
<div>
<label for="username">Username</label><span id="user_info"
class="error-info"></span>
</div>
<div>
<input name="user_name" id="user_name" type="text"
class="demo-input-box" placeholder="Enter Username or Email">
</div>
</div>
<div class="field-column">
<div>
<label for="password">Password</label><span id="password_info"
class="error-info"></span>
</div>
<div>
<input name="password" id="password" type="password"
class="demo-input-box" placeholder="Enter Password">
</div>
</div>
<div class=field-column>
<div>
<input type="submit" name="login" value="Login" class="btnLogin"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-nav-row">
<a href="#" class="form-link">Forgot password?</a>
</div>
<div class="login-row form-nav-row">
<p>New user?</p>
<a href="#" class="btn form-link">Signup Now</a>
</div>
<div class="login-row form-nav-row">
<p>May also signup with</p>
<a href="#"><img src="view/images/icon-facebook.png"
class="signup-icon" /></a><a href="#"><img
src="view/images/icon-twitter.png" class="signup-icon" /></a><a
href="#"><img src="view/images/icon-linkedin.png"
class="signup-icon" /></a>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<script>
function validate() {
var $valid = true;
document.getElementById("user_info").innerHTML = "";
document.getElementById("password_info").innerHTML = "";
var userName = document.getElementById("user_name").value;
var password = document.getElementById("password").value;
if(userName == "")
{
document.getElementById("user_info").innerHTML = "required";
$valid = false;
}
if(password == "")
{
document.getElementById("password_info").innerHTML = "required";
$valid = false;
}
return $valid;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
PHP login form action
A PHP endpoint script that is an action target of the login form handles the login data.
This login page in PHP sanitizes the data before processing them. It uses PHP filter_var function to sanitize the user entered authentication details.
It conducts the authentication process after receiving the user credentials.
This program puts the authenticated user details in a session. Then, it acknowledges the user accordingly.
login-action.php
<?php
namespace Phppot;
use \Phppot\Member;
if (! empty($_POST["login"])) {
session_start();
$username = filter_var($_POST["user_name"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
$password = filter_var($_POST["password"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
require_once (__DIR__ . "/class/Member.php");
$member = new Member();
$isLoggedIn = $member->processLogin($username, $password);
if (! $isLoggedIn) {
$_SESSION["errorMessage"] = "Invalid Credentials";
}
header("Location: ./index.php");
exit();
}
PHP login authentication model class
It contains the processLogin() function to check the PHP login form data with the database. It uses PHP password_verify() function to validate the user-entered password. This PHP function compares the password with the hashed password on the database.
The getMemberById() function reads the member result by member id. After successful login, it is called from the case to display the dashboard. It returns the array of data to be displayed on the dashboard.
class/Member.php
<?php
namespace Phppot;
use \Phppot\DataSource;
class Member
{
private $dbConn;
private $ds;
function __construct()
{
require_once "DataSource.php";
$this->ds = new DataSource();
}
function getMemberById($memberId)
{
$query = "select * FROM registered_users WHERE id = ?";
$paramType = "i";
$paramArray = array($memberId);
$memberResult = $this->ds->select($query, $paramType, $paramArray);
return $memberResult;
}
public function processLogin($username, $password) {
$query = "select * FROM registered_users WHERE user_name = ? OR email = ?";
$paramType = "ss";
$paramArray = array($username, $username);
$memberResult = $this->ds->select($query, $paramType, $paramArray);
if(!empty($memberResult)) {
$hashedPassword = $memberResult[0]["password"];
if (password_verify($password, $hashedPassword)) {
$_SESSION["userId"] = $memberResult[0]["id"];
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
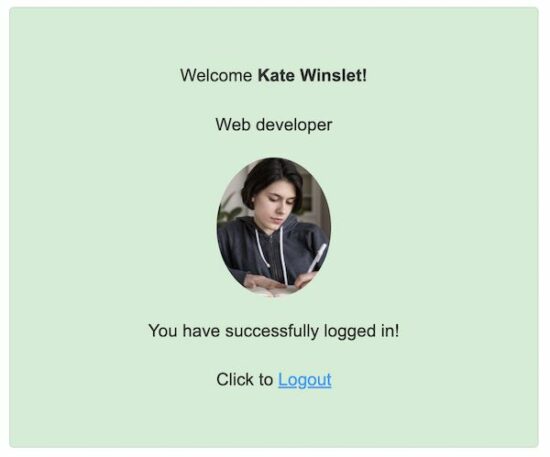
Show dashboard and logout link after PHP login
After successful login, the site says there exists a session of the logged-in user. It can be shown in different ways.
In most sites, the site header displays the logged-in user’s profile link. It can be a clickable avatar that slides down a profile menu.
This PHP login system redirects the user to a dashboard page after login. This dashboard page shows a welcome message, about-user with an avatar.
The landing page checks the PHP session if any user has already login. If so, it will redirect to this dashboard page.
view/dashboard.php
<?php
namespace Phppot;
use \Phppot\Member;
if (! empty($_SESSION["userId"])) {
require_once __DIR__ . './../class/Member.php';
$member = new Member();
$memberResult = $member->getMemberById($_SESSION["userId"]);
if(!empty($memberResult[0]["display_name"])) {
$displayName = ucwords($memberResult[0]["display_name"]);
} else {
$displayName = $memberResult[0]["user_name"];
}
}
?>
<html>
<head>
<title>User Login</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial;
color: #333;
font-size: 0.95em;
}
.dashboard {
background: #d2edd5;
margin: 15px auto;
line-height: 1.8em;
color: #333;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 30px;
max-width: 400px;
border: #c8e0cb 1px solid;
text-align: center;
}
a.logout-button {
color: #09f;
}
.profile-photo {
width: 100px;
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="dashboard">
<div class="member-dashboard">
<p>Welcome <b><?php echo $displayName; ?>!</b></p>
<p><?php echo $memberResult[0]["about"]; ?></p>
<p><img src="./view/images/photo.jpeg" class="profile-photo" /></p>
<p>You have successfully logged in!</p>
<p>Click to <a href="./logout.php" class="logout-button">Logout</a></p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Logging out from the site
This is a general routine to log out from the site. The following script clears the PHP session. Then it redirects back to login page in PHP.
Sometimes, the logout case may clear cookies. Example: In the case of using a cookie-based Remember Me feature in login.
view/dashboard.php
<?php
session_start();
$_SESSION["user_id"] = "";
session_destroy();
header("Location: index.php");
Files structure
See the below image that shows the file structure of this simple PHP login form example. It contains a featured login form UI with the application view files.
The login action calls the PHP model on the submit event. It performs backend authentication with the database.
Database script
Look at this SQL script which contains the CREATE statement and sample row data.
By importing this SQL, it creates database requisites in your development environment.
The sample data helps to try a login that returns success response on the authentication.
Test data: username: kate_91 password: admin123
sql/database.sql
--
-- Database: `blog_eg`
--
-- --------------------------------------------------------
--
-- Table structure for table `registered_users`
--
CREATE TABLE `registered_users` (
`id` int(8) NOT NULL,
`user_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`display_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`photo` text DEFAULT NULL,
`about` text DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
--
-- Dumping data for table `registered_users`
--
INSERT INTO `registered_users` (`id`, `user_name`, `display_name`, `password`, `email`, `photo`, `about`) VALUES
(1, 'kate_91', 'Kate Winslet', '$2y$10$LVISX0lCiIsQU1vUX/dAGunHTRhXmpcpiuU7G7.1lbnvhPSg7exmW', 'kate@wince.com', 'images/photo.jpeg', 'Web developer');
--
-- Indexes for dumped tables
--
--
-- Indexes for table `registered_users`
--
ALTER TABLE `registered_users`
ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id`);
--
-- AUTO_INCREMENT for dumped tables
--
--
-- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `registered_users`
--
ALTER TABLE `registered_users`
MODIFY `id` int(8) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, AUTO_INCREMENT=2;
Secure DataSource using MySQL with prepared statements
This DataSource is a common file to be used in any stand-alone PHP application. It uses MySQLi with prepared statement to execute database queries. It works with PHP 8 and 7+
class/DataSource.php
This class is available in the project download zip file below. It is a common wrapper for MySQL using PreparedStatement.
Conclusion
We have seen a simple example on the PHP login form. Hope this will be useful to have a featured, responsive login form.
The article interlinks the constellations of a login form. It will be helpful to integrate more features with the existing login template.
Let me know your feedback on the comments section if you need any improvements on this PHP login system.

Thanks a lot
All your script are awesome, simple and beautifull! ;)
Thanks
Welcome Bob.
It would be great if you create a tutorial on how to login and register with Google and Facebook on a website
Hi Erick,
I have already written tutorials on them. Please use the search bar in the header and you will land in it easily. Thanks.