Integrating Google Maps into a React app is a powerful location-based feature. It helps for live user tracking to delivery routes, geo-fencing, and real-time movement progression. It is one of the simplest jobs with the help of the Google Maps JavaScript API and React libraries.
Real-time location tracking improves the usability of your apps. It can be implemented for dashboards, for tracking location on Duty, or anything that involves dynamic location-based requirements.
This React example helps to integrate Google Maps into React. It renders dynamic maps to the UI and displays markers to pinpoint the live location. It continuously updates the user’s position using the browser’s Geolocation API.
![]()
Google Maps Integration steps
These are the few steps to enable required Google API services and configure the key credentials with the React App. This process builds a channel between the enduser and the Google cloud services for which they are registered with.
- Login with Google Cloud Console and create a new project.
- Choose APIs and Services and enable Maps JavaScript API.
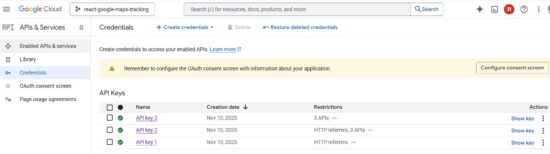
- Go to Credentials menu and CREATE CREDENTIALS -> API Key to generate API key.
- Install React Google Maps library in your app using
npm install @react-google-maps/api. - Configure this key to your React app when loading React Google Maps JS library.
The credentials page shows the list of API keys generated. You can restrict the keys for specific domains or for using particular Google API services.
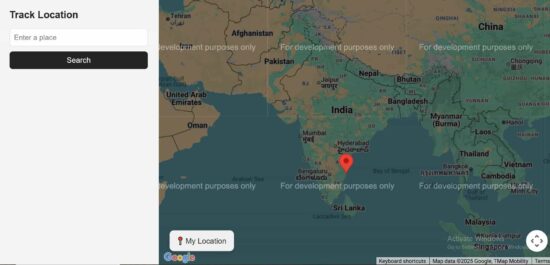
Rendering Google Maps with current location
The TrackLocation JSX shows HTML components for displaying the Google Map and a location search option.
If the location search is not applied, it is showing the marker on the users current location.
src/components/TrackLocation.jsx
import { useState } from "react";
import SearchBox from "./SearchBox";
import MapContainerComponent from "./MapContainerComponent";
export default function TrackLocation() {
const [searchQuery, setSearchQuery] = useState("");
return (
<div style={{ display: "flex" }}>
<SearchBox onSearch={setSearchQuery} />
<MapContainerComponent searchQuery={searchQuery} />
</div>
);
}
React Google Maps Component
This is the main component which initiates the React Google Maps library by configuring the Google Cloud API service key.
It manages React states for having the Map instance, map marker location and the searched location. The marker location is depends on two factors. It will be changed dynamically to show the real-time location of the user. Also, it is changed when the search is applied.
With the help of the client side Geo location capabilities, navigator.geolocation gets the latitude and longitude of the user’s position. Then it is used to build the location object to plot the marker to the map.
src/components/MapContainerComponent.jsx
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { GoogleMap, useJsApiLoader } from "@react-google-maps/api";
import LocationMarker from "./LocationMarker";
export default function MapContainerComponent({ searchQuery }) {
const [map, setMap] = useState(null);
const [userLocation, setUserLocation] = useState(null);
const [searchLocation, setSearchLocation] = useState(null);
const { isLoaded } = useJsApiLoader({
googleMapsApiKey: "YOUR API KEY",
libraries: ["places"],
});
useEffect(() => {
if (navigator.geolocation) {
const watchId = navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(
(pos) => {
const newLoc = {
lat: pos.coords.latitude,
lng: pos.coords.longitude,
};
setUserLocation(newLoc);
if (map && !searchLocation) {
map.setCenter(newLoc);
map.setZoom(13);
}
},
(err) => console.error("Location error:", err),
{ enableHighAccuracy: true, maximumAge: 1000 }
);
return () => navigator.geolocation.clearWatch(watchId);
} else {
console.error("Geolocation not supported");
}
}, [map, searchLocation]);
useEffect(() => {
if (!searchQuery || !window.google || !map) return;
const geocoder = new window.google.maps.Geocoder();
geocoder.geocode({ address: searchQuery }, (results, status) => {
if (status === "OK" && results[0]) {
const loc = results[0].geometry.location;
const newSearchLoc = { lat: loc.lat(), lng: loc.lng() };
setSearchLocation(newSearchLoc);
if (userLocation) {
const bounds = new window.google.maps.LatLngBounds();
bounds.extend(userLocation);
bounds.extend(newSearchLoc);
map.fitBounds(bounds);
} else {
map.setCenter(newSearchLoc);
map.setZoom(12);
}
} else {
console.warn("Location not found for:", searchQuery);
}
});
}, [searchQuery, map, userLocation]);
const zoomToLocation = (loc) => {
if (!map || !loc) return;
map.panTo(loc);
map.setZoom(15);
};
return (
<div className="map-container">
{isLoaded && (
<GoogleMap
mapContainerStyle={{ width: "100%", height: "100vh" }}
center={userLocation || { lat: 20.5937, lng: 78.9629 }}
zoom={userLocation ? 13 : 5}
onLoad={setMap}
options={{
streetViewControl: false,
mapTypeControl: false,
fullscreenControl: false,
}}>
<LocationMarker
position={userLocation}
title="Your Location"
onClick={() => zoomToLocation(userLocation)}
/>
<LocationMarker
position={searchLocation}
title="Tracked Location"
onClick={() => zoomToLocation(searchLocation)}
/>
</GoogleMap>
)}
{userLocation && (
<button
className="floating-btn"
onClick={() => zoomToLocation(userLocation)}>
My Location
</button>
)}
</div>
);
}
This LocationMarker component is part of the main React component that accepts the users location or searched location. It pins the marker to the Map based on the location details.
src/components/LocationMarker.js
import React from "react";
import { Marker } from "@react-google-maps/api";
export default function LocationMarker({ position, title, onClick }) {
return position ? <Marker position={position} title={title} onClick={onClick} /> : null;
}
Google Maps Search feature
The search form contains interface to enter the place to mark on the Map. When the search is applied, the LocationMarker rendered with the position:searchLocation shows the marker on the right place.
src/components/SearchBox.jsx
import { useState } from "react";
export default function SearchBox({ onSearch }) {
const [query, setQuery] = useState("");
const handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (query.trim()) onSearch(query);
};
return (
<div className="search-sidebar">
<h3 className="sidebar-title">Track Location</h3>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Enter a place"
value={query}
onChange={(e) => setQuery(e.target.value)}
className="search-input"
/>
<button type="submit" className="search-btn">
Search
</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}
Conclusion
Real-time location tracking in React becomes easy with the joint capabilities of the Geolocation API and Google Maps. It changes the user’s position on movement. This example enriches user experience with a live movement tracking feature. And, it will be easy to use in a location-based React application that needs to render users’ live locations.
References:
