How to Handle CSV with PHP: Read Write, Import Export with Database
CSV is one of the familiar file formats and used widely by programmers for handling data. The simplicity of the format and human readable form made it so popular. CSV stands for Comma-Separated Values. In earlier days, the delimiter was only a comma (,) and so the name CSV. Nowadays, CSV files use tab-demitted row data too.
To handle CSV with PHP, we must be aware there is excellent support in-built with core PHP. Knowledge about those built-in library and functions will he handy in handling CSV files.

What is inside?
In this article, we will see about about how to handle CSV using PHP with suitable examples.
- CSV file format and MIME type
- How to convert PHP Array to CSV?
- CSV file data validation
- How to import large CSV files?
- How to split large CSV files and process using PHP?
- How to read encoded CSV files with special characters?
- Convert CSV file to HTML table using PHP
- Process CSV file with comma data values using PHP
- Export database records to CSV in a generic way
- How to export CSV using fputcsv?
- Download as CSV File via browser using Content-Type
- Read CSV using PHP built-in functions
This will serve you as a comprehensive tutorial that discusses all aspects of CSV file handling with PHP. When you need to handle structured data then using JSON data and handling it with PHP will be a better choice.
CSV file format and MIME type
Let us start with CSV format and MIME type conventions. The common formats and MIME type for the CSV files are discussed here with the reference of the RFC 4180 documentation.
CSV Format Definition
These are the general definitions for a valid CSV format.
- Each row is separated or delimited by a line break (CRLF). For example:
col_11,col_12,col_13 CRLF col_21,col_22,col_23 CRLF - The last row of the CSV file may or may not have a line break. For example:
col_11,col_12,col_13 CRLF col_21,col_22,col_23 - CSV data may contain an optional header line at the beginning in the same format as other rows. For example:
column_name1,column_name2,column_name3 CRLF col_11,col_12,col_13 CRLF col_21,col_22,col_23 - The count of the comma-separated field names in the header must be the same as the count of the comma-separated values in rest of the rows in the CSV file. For example:
column_name1,column_name2,column_name3 CRLF col_11,col_12,col_13 CRLF col_21,col_22,col_23 - Each field the rows may be enclosed by Double Quotes(“). But it is optional. Fields not enclosed by double quote may not contain the double quotes special character as part of it. For example:
"col_11","col_12","col_13" CRLF col_21,col_22,col_23 - Fields containing double quotes (“), Line Break (CRLF) and Comma must be enclosed with double quotes. For example:
"col_""11","col_"CRLF 12",col_13 CRLF col_21,col_22,col_23 - Fields containing double quotes (“), Line Break (CRLF) and Comma must be enclosed with double quotes. For example:
"col_11","col_"CRLF 12",col_13 CRLF col_21,col_22,col_23 - If Fields enclosed by double quotes (“) contain double quotes character then the double quotes inside the field must be preceded with another double quote as an escape sequence. For example:
"col_""11","col_12",col_13 CRLF col_21,col_22,col_23
The standard exclusive MIME type text/csv is registered by the RFC 4180. Before that, various MIME types like “text/tab-separated-values” type were used by various programs or OS for the CSV format.
If you want to learn more about the CSV format and MIME types, the RFC 4180 document has more information.
How to convert PHP Array to CSV?
There are many possible ways in PHP to convert an array data into CSV format. PHP contains in-built functions like fputcsv() for doing this conversion.
The following code uses custom PHP function str_putcsv() to get the array data and put it into the file target as specified. This custom function uses PHP built-in fputcsv() on each array iteration.
<?php
function arrayToCSV($inputArray)
{
$csvFieldRow = array();
foreach ($inputArray as $CSBRow) {
$csvFieldRow[] = str_putcsv($CSBRow);
}
$csvData = implode("\n", $csvFieldRow);
return $csvData;
}
function str_putcsv($input, $delimiter = ',', $enclosure = '"')
{
// Open a memory "file" for read/write
$fp = fopen('php://temp', 'r+');
// Write the array to the target file using fputcsv()
fputcsv($fp, $input, $delimiter, $enclosure);
// Rewind the file
rewind($fp);
// File Read
$data = fread($fp, 1048576);
fclose($fp);
// Ad line break and return the data
return rtrim($data, "\n");
}
$inputArray = array(
array("First Name", "Last Name", "Identification Number"),
array("Kim","Thomas","8001"),
array("Jeffery","Robert","8021"),
array("Helan","Albert","8705")
);
print "<PRE>";
print $CSVData = arrayToCSV($inputArray);
?>
I have printed the converted output data to the browser. The CSV output is,

CSV file data validation
Generally, validation on a CSV file will be done to check whether it has the standard format definition. The following conditions have to be applied to a CSV input file to check whether it is valid or not.
- To check if the input file is with the proper CSV file extension and within the size limit.
- To check if the count of comma-separated values in all rows are same.
- To check if the row data containing allowed special characters with proper escape sequences.
Added to that, you can add additional validation based on your application requirement. For example,
- To check if the CSV row field contains data in an expected format. For example, if a phone_number field contains numeric data with allowed characters.
- To check if the fields are in the correct order as per your application requirement.
- To check if the mandatory fields are not empty.
This PHP code shows how to apply CSV validation on an uploaded file. In a previous tutorial, we have seen how to validate an uploaded image file in PHP.
In this script, the validation made to check the CSV file extension, size. Once it is done, we need to handle CSV with PHP to check the field count in all the CSV rows.
<?php
if (isset($_POST["upload"])) {
// Get file extension
$file_extension = pathinfo($_FILES["file-input"]["name"], PATHINFO_EXTENSION);
// Validate file input to check if is not empty
if (! file_exists($_FILES["file-input"]["tmp_name"])) {
$response = array(
"type" => "error",
"message" => "File input should not be empty."
);
} // Validate file input to check if is with valid extension
else if ($file_extension != "csv") {
$response = array(
"type" => "error",
"message" => "Invalid CSV: File must have .csv extension."
);
echo $result;
} // Validate file size
else if (($_FILES["file-input"]["size"] > 2000000)) {
$response = array(
"type" => "error",
"message" => "Invalid CSV: File size is too large."
);
} // Validate if all the records have same number of fields
else {
$lengthArray = array();
$row = 1;
if (($fp = fopen($_FILES["file-input"]["tmp_name"], "r")) !== FALSE) {
while (($data = fgetcsv($fp, 1000, ",")) !== FALSE) {
$lengthArray[] = count($data);
$row ++;
}
fclose($fp);
}
$lengthArray = array_unique($lengthArray);
if (count($lengthArray) == 1) {
$response = array(
"type" => "success",
"message" => "File Validation Success."
);
} else {
$response = array(
"type" => "error",
"message" => "Invalid CSV: Count mismatch."
);
}
}
}
?>
CSV Validation Script
<form id="frm-upload" action="" method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
<div class="form-row">
<div>Choose file:</div>
<div>
<input type="file" class="file-input" name="file-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="button-row">
<input type="submit" id="btn-submit" name="upload"
value="Upload">
</div>
</form>
<?php if(!empty($response)) { ?>
<div class="response <?php echo $response["type"]; ?>
">
<?php echo $response["message"]; ?>
</div>
<?php }?>
If the validation process is not returning TRUE then the error message will be displayed to the user as shown in the below screenshot.
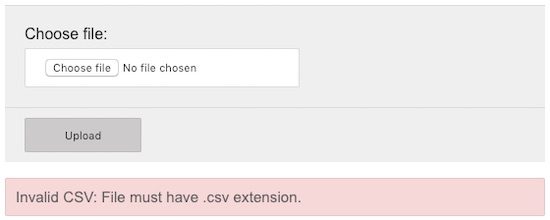
How to import large CSV files?
Importing a large CSV file using PHP file handling functions may not be an efficient way of doing it. If the execution time exceeds the configured max_execution_time limit then the import will not be completed.
While processing large CSV file import, there are ways like command line execution, query execution and more. In this section, I will show how to import a large CSV file using MySQL LOAD DATA statement. If you can this LOAD, then this is the better choice as it gives the best performance.
<?php
$conn = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "test", "blog_samples");
$query = "LOAD DATA INFILE 'input.csv' INTO TABLE tbl_student_master IGNORE 1 LINES";
if (!mysqli_query($conn, $query)) {
printf("Errormessage: %s\n", mysqli_error($conn));
}
?>
Before running this program, make sure that you have created the required target database and table. Import the following SQL script to process import by running this example in your environment.
--
-- Table structure for table `tbl_student_master`
--
CREATE TABLE `tbl_student_master` (
`unique_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`first_name` varchar(55) NOT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(55) NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
--
-- Indexes for table `tbl_student_master`
--
ALTER TABLE `tbl_student_master`
ADD PRIMARY KEY (`unique_id`);
COMMIT;
Note: If the –secure-file-priv option is enabled in your MySQL configuration, then this program will work only if the input CSV file is located in the directory as specified in the –secure-file-priv settings.
How to split large CSV files and process using PHP?
In a previous tutorial, we have seen how to split an excel file into multiple files. Splitting will be required while dealing with large Excel or CSV file.
In this section, I am showing how to split a CSV file into multiple files. I have used PHP RegexIterator and SplFileObject classes for implementing splitting on an input CSV file.
The RegexIterator is the built-in PHP class that inherits FilterInheritor class to filter based on regular expression. It accepts the input data, regex pattern and mode of operations and more parameters.
The SplFileObject class which gives an object-oriented interface for a file. Using this the target object is created to put the splitted records into the target.
<?php
$rowAry = new \RegexIterator(new \SplFileObject('input.csv'), '/\n/', RegexIterator::SPLIT);
$header = "";
foreach ($rowAry as $i => $row) {
// IF the input CSV has header (column_name) row
if ($i == 0) {
$header = $row[0];
} else {
$filename = "output_$i.csv";
$myfile = fopen($filename, "w");
$target = new \SplFileObject($filename, 'w');
if (! empty($header)) {
$target->fwrite($header . "\n");
}
$target->fwrite($row[0]);
}
}
?>
How to read encoded CSV files with special characters?
If the input CSV contains non-english data, the CSV file parsing will behave as expected. Either it will return error like “Invalid argument” or it will output jumbled character as the result of the CSV read operation.
This issue could be resolved by setting the charset while reading CSV. In the below script, the PHP iconv function is used to set the input and output charset for reading the actual data from the CSV.
<?php
function convert( $str ) {
return iconv( "UTF-8", "UTF-8", $str );
}
if (($fp = fopen('input.csv', "r")) !== FALSE) {
while (($row = fgetcsv($fp)) !== false) {
$rowArray = array_map( "convert", $row );
$rowCSV[] = implode(",", $rowArray);
}
fclose($fp);
$csvData = implode("\n", $rowCSV);
print $csvData;
}
?>
Convert CSV file to HTML table using PHP
For converting the CSV file into a HTML format, the table rows markup has to be created during the row by row iteration of the CSV.
With the reference of the previous examples that we have seen above, it is an easy job to create HTML for the CSV data.
Below code shows how to generate HTML table markup and display the CSV data into it. It iterates the CSV file uploaded via an HTML form and it is parsed to get the row data.
The parsed row data is put into the table columns by using PHP echo statements. The table header could be identified by using the loop iteration index. Hence, the header data is differentiated from the other rows using CSS.
<?php
if(!empty(isset($_POST["upload"]))) {
if (($fp = fopen($_FILES["file-input"]["tmp_name"], "r")) !== FALSE) {
?>
<table class="tutorial-table" width="100%" border="1" cellspacing="0">
<?php
$i = 0;
while (($row = fgetcsv($fp)) !== false) {
$class ="";
if($i==0) {
$class = "header";
}
?>
<tr>
<td class="<?php echo $class; ?>"><?php echo $row[0]; ?></td>
<td class="<?php echo $class; ?>"><?php echo $row[1]; ?></td>
<td class="<?php echo $class; ?>"><?php echo $row[2]; ?></td>
</tr>
<?php
$i ++;
}
fclose($fp);
?>
</table>
<?php
$response = array("type" => "success", "message" => "CSV is converted to HTML successfully");
} else {
$response = array("type" => "error", "message" => "Unable to process CSV");
}
}
?>
</div>
<?php if(!empty($response)) { ?>
<div class="response <?php echo $response["type"]; ?>
">
<?php echo $response["message"]; ?>
</div>
<?php } ?>
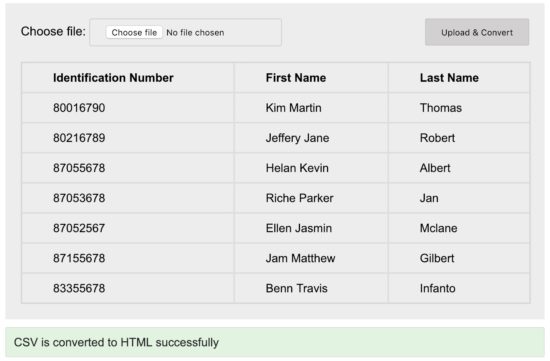
CSV to HTML Conversion Output
The following screenshot shows the output of the HTML table generated by parsing the CSV file uploaded via the form.
Process CSV file with comma data values using PHP
As per the CSV specification “Fields containing line breaks (CRLF), double quotes, and commas should be enclosed in double-quotes.
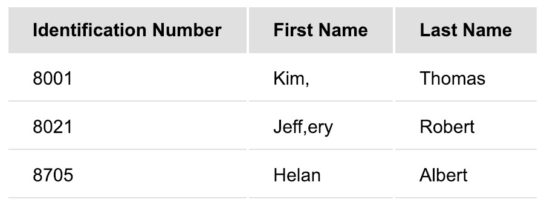
So, I have created an input.csv containing values with Comma(,) character. The file content will be as shown as below.
"Identification Number","First Name","Last Name"
8001,"Kim,",Thomas
8021,"Jeff,ery",Robert
8705,Helan,Albert
In the above CSV data, you can see that the values containing Comma are enclosed by the double quotes(“)
As like as the above example, we are going to use PHP fgetcsv() function to read and process the CSV file data containing Comma in its value.
As per the syntax of the fgetcsv() function, it receives character inputs for specifying the field delimiter, field enclosure and more.
As the default enclosure is the double quotes character, we need not specify those parameters while invoking fgetcsv().
Supply the CSV input having values with Comma to the CSV to HTML conversion script that we have seen in the above section. This will output the CSV data with Comma in the HTML format as shown below.
Export database records to CSV in a generic way
While exporting a database, the backup file can be created in various formats SQL, CSV, Excel. In a previous tutorial, we have seen how to export a database to a CSV file.
For doing this database backup programmatically, we need to execute appropriate MySQL statements to extract the structure and the data.
By doing this, the backup will be ready with the database table’s create statements, insert queries dumped with data, statements for Indexes, auto increment and more. The PHP code for exporting database records to CSV is as follows.
<?php
$conn = mysqli_connect("localhost","root","test", "phppot_examples");
$query = "SELECT * FROM toy";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $query);
$num_column = mysqli_num_fields($result);
$csv_header = '';
for($i=0;$i<$num_column;$i++) {
$csv_header .= '"' . mysqli_fetch_field_direct($result,$i)->name . '",';
}
$csv_header .= "\n";
$csv_row ='';
while($row = mysqli_fetch_row($result)) {
for($i=0;$i<$num_column;$i++) {
$csv_row .= '"' . $row[$i] . '",';
}
$csv_row .= "\n";
}
?>
In this code, the database structure and data are extracted and prepared in the form of CSV string.
Then the prepared backup content can be downloaded to the browser by using PHP header() function with the specification if Content-Type. In the following sections, we will see how to download CSV by using Content-Type.
How to export CSV using fputcsv?
If you are only going to take the data backup instead of a complete database, then the fputcsv() function is enough. This function accepts the target CSV handle and the input array as it mandatory arguments.
The input array must contain the row of column names or column values. The following PHP code shows how to exports MySQL records to a CSV file using fputcsv().
In this code, the database column names and values are extracted row by row and put it into the target CSV. The target CSV handle is created before executing the fputcsv() function.
<?php
$conn = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "test", "phppot_examples");
$filename = "toy_csv.csv";
$fp = fopen('php://output', 'w');
$query = "SELECT COLUMN_NAME FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='phppot_examples' AND TABLE_NAME='toy'";
$result = mysqli_query($conn,$query);
while ($row = mysqli_fetch_row($result)) {
$header[] = $row[0];
}
header('Content-type: application/csv');
header('Content-Disposition: attachment; filename='.$filename);
fputcsv($fp, $header);
$query = "SELECT * FROM toy";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $query);
while($row = mysqli_fetch_row($result)) {
fputcsv($fp, $row);
}
exit;
?>
Download as CSV File via browser using Content-Type
In the above code, the PHP header() function is used to specify the Content-type, Content-disposition and more specifications. With these settings, the header will be sent to the browser with the CSV file attachment to be downloaded.
By adding the header() function with Content-type: application/csv then CSV file will be downloaded to the browser.
Read CSV using PHP built-in functions
PHP supports to read a CSV file by proving built-in functions. In this article, we have seen several examples to handle CSV with PHP functions like fgetcsv(), str_getcsv(). All these PHP functions are used in the above sections to read CSV file before processing it.
The fgetcsv() function is used to read the CSV file data with the reference of the file handle. The str_getcsv() will accept the CSV string instead of the file pointer. Then the CSV string will be parsed to read the data.
Conclusion
As the CSV(Comma-Separated Values) is one of the popularly used data handling formats and every programmer should be comfortable in handling CSV data. PHP provides the best support for handling CSV file and you should be aware of the functions available. Hope you have been introduced to all about CSV in PHP. If there is any topic missing, let me know it via the comments below and I will include that in the article.

I am tasked to process census records. I was looking for a way to process the huge volume and mysql load way you have described is cool. Thanks.
Welcome Liam. I am glad that it is of help to you.
Almost all your code are simple and clean without any bloatware, no unnecessary dependency. Straight to the point and minimal number of lines. Appreciations to you, continue the good job.
With thanks, from Milan.
Sure Willie, thank you for the nice words and I will be continuing it.
can you write one similar on excel?
Sure Hank, I will soon write one similar article on processing excel files using PHP.
Hey, Vincy I am a very big fan of you.
Please when you prepare import/export on excel, please can you give us the best strategy for a very huge database? because last time I have tried but was failed on it using ajax-PHP-MySQL-Phpspreadsheet.
Is it the best approach for using batch processing?
That is so nice of you Pr.
Sure, I will include a section on handling huge excel files.
Thanks for your contributions nice one.
You are most welcome Jafar.
Big THANKS 2U. Your code always help, Am becoming better in coding due to some of your codes. None of your code is ever useless, it help always. THANK YOU.
Please provide fast means of communicating with you for freelance work.
Thank you for the very nice words Abdulrasheed. It is so nice of you. You can contact me via my email vincy@phppot.com for freelance services and I always respond within a day.
Words are not enough for me to appreciate your efforts. I’ve benefited a lot from this site. You’re so kind for sharing your knowledge FREE. I pray for more knowledge and wisdom. Thank you. Please check your mail, I sent you a message to help me out on Uploading and Inserting CSV into MySql. Than you so much.
Thank you so much for the nice words Opeyemi. I will check my email and reply to you on that.
Alright. I’ll be waiting
Great job! Vincy :) God Bless
Thank you Sameer for the appreciations.
Welcome Imam.
i have to save CSV to specific path via ajax request
Yes it is definitely possible but you need to make some code tweaks. AJAX request and saving to a path are two different things and can be handled independently.
thank you very much
Welcome Jafar.
Your method of explanation and code writing is so simple, narrative and clean which makes laymen like us to understand every piece of it!
Brilliant work, please let me know if I can be of any help to you. I have a dedicated server which I can lend it to you at the lowest price or even free if we agree to terms.
Hi Aatmik,
Thank you for the nice words and thank you for the offer on server. I will definitely let you know if I need one. Thanks a lot.
Excellent work Vincy. Very knowledgeable. I’ve benefited a lot from this article. I want to know few other things,
1. I have a csv file and I want to edit a filed (column value) of a particular row and save it with php.
2. Want to delete a particular row.
Thanks in advance.
Welcome Jai, thank you for the nice words.
This will require custom code. I will try to enhance the code and update it in the article.
thank you very much bro
Excellent article. It helped me to identify one problem with double quotes. But I am not able to solve it: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/72439722/how-to-use-fgetcsv-when-the-csv-has-four-double-quotes-for-empty-fields
Why is the entire line enclosed with quotes? Even though there are several entries and not one. Is the CSV corrupted (see Stackoverflow).
Thanks in advance for your help!