MySQL “ORDER BY” clause is used to order results based on a column. This clause is used in select queries to do sort by specifying the column order (ASC, DESC). If no order is given, then ASC is the default order. Syntax,
SELECT * FROM table_name ORDER BY column_name desc
Using the “ORDER BY” clause we can get ordered results based on multiple columns.
Example: Sorting MySQL Table Records using ORDER BY
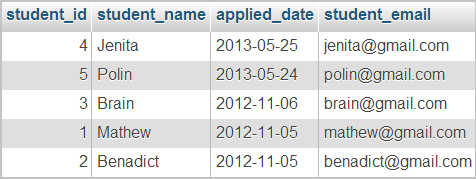
This is the student table containing student_name, student_email and applied_date columns.
First, we are going to write a query to order this table data by using a single column student_name in descending order. The query is like,
SELECT * FROM students ORDER BY student_name DESC
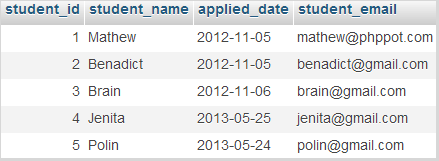
After running this query, the student’s table results will be as,
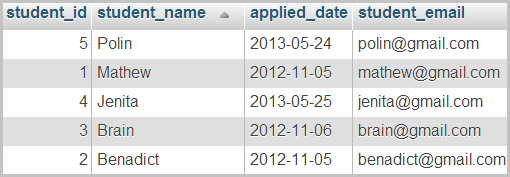
Next, we are writing a query in order by two columns applied_date and student_name. The query is,
SELECT * FROM students ORDER BY applied_date DESC, student_name DESC
This query will sort students’ records in descending order. If any number of these records have the same value for applied_date, then, these records will be sorted by the student_name column in descending order. Now, the result is,